Now Reading: SG90 Servo Motor with ESP32 DOIT Kit v1
-
01
SG90 Servo Motor with ESP32 DOIT Kit v1
SG90 Servo Motor with ESP32 DOIT Kit v1

Introduction
The SG90 servo motor is a lightweight and low-cost motor commonly used in robotics, IoT, and automation projects. Unlike DC motors, which rotate continuously, a servo motor can be controlled to move to a specific angle (0°–180°) with great precision.
The ESP32, with its PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) capability, is perfect for controlling servo motors. By sending PWM signals, the servo can be positioned at any desired angle.
In this tutorial, we will connect the SG90 servo motor to ESP32 DOIT Kit v1 and control its rotation using Arduino IDE.
Components Required
- ESP32 DOIT Kit v1
- SG90 Servo Motor
- Jumper Wires
- External Power Supply (optional, for stable operation)
- Breadboard
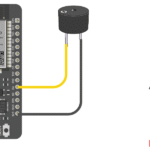
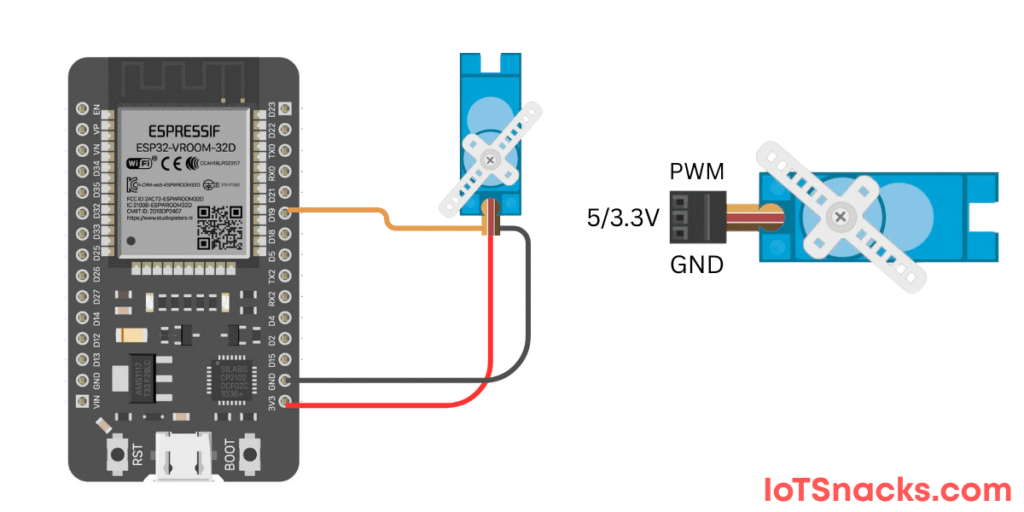
Pin Connections
| SG90 Servo Pin | ESP32 Pin |
|---|---|
| VCC (Red) | 5V |
| GND (Brown) | GND |
| Signal (Orange) | GPIO 19 |
⚠️ Note: The servo may draw more current than the ESP32 can supply. If the servo behaves erratically, use an external 5V supply (but connect grounds together).
Arduino Code
#include <ESP32Servo.h>
// Create servo object
Servo myServo;
void setup() {
// Attach servo to GPIO19
myServo.attach(19);
myServo.write(0);
}
void loop() {
// Rotate from 0° to 180°
for (int angle = 0; angle <= 180; angle++) {
myServo.write(angle); // Move to 'angle'
delay(15); // Delay for smooth movement
}
// Rotate back from 180° to 0°
for (int angle = 180; angle >= 0; angle--) {
myServo.write(angle);
delay(15);
}
}
Step-by-Step Code Explanation
#include <ESP32Servo.h>→ Includes the Servo library to control servo motors.Servo myServo;→ Creates a servo object.myServo.attach(19);→ Connects the servo to GPIO 19.myServo.write(0);→ Set the Angle to 0°- Loop Section → First rotates the servo from 0° to 180°, then back from 180° to 0° with small delays for smooth movement.
Real-Life Applications
- Robotic arms and joints
- Camera pan & tilt systems
- IoT-controlled door locks
- Automated solar trackers
- Mini CNC or robotic cars
Troubleshooting
- Servo not moving → Check wiring and ensure correct GPIO pin.
- Jerky movement → Use external 5V power supply for stable operation.
- ESP32 rebooting → Caused by high current draw; use external power.
- Limited rotation → SG90 is a positional servo (0°–180°), not continuous.
Can I power the SG90 directly from ESP32 3.3V?
No, it is recommended to power the servo from 5V for reliable operation.
Can I connect multiple SG90 servos to ESP32?
Yes, ESP32 has multiple PWM pins. But for more than 2–3 servos, use an external power source.
Why is my servo jittering when idle?
This is usually due to PWM signal interference or insufficient power. Adding a capacitor across power lines can help.
Can I control servo position with a potentiometer on ESP32?
Yes, you can read analog input from a potentiometer and map it to servo angles.
Can I use SG90 for continuous rotation?
No, SG90 is a positional servo (0°–180°). For continuous rotation, use a different type of servo.