Now Reading: LDR with ESP8266: Measure Light Intensity Step by Step
-
01
LDR with ESP8266: Measure Light Intensity Step by Step
LDR with ESP8266: Measure Light Intensity Step by Step

Introduction
The LDR (Light Dependent Resistor) is a simple but powerful sensor that detects light intensity. Its resistance decreases when light falls on it, and increases in darkness. By connecting an LDR with an ESP8266 Wi-Fi microcontroller, you can build smart IoT projects like:
- Automatic street lights
- Smart lamps
- Light-based alarms
- Data logging of light levels
In this tutorial, you’ll learn how to connect an LDR with ESP8266, read light levels in Arduino IDE, and understand the code step by step.
What You Need
- ESP8266 board (NodeMCU, Wemos D1 Mini, etc.)
- LDR (Light Dependent Resistor)
- 10kΩ resistor (for voltage divider)
- Breadboard & jumper wires
- Arduino IDE installed
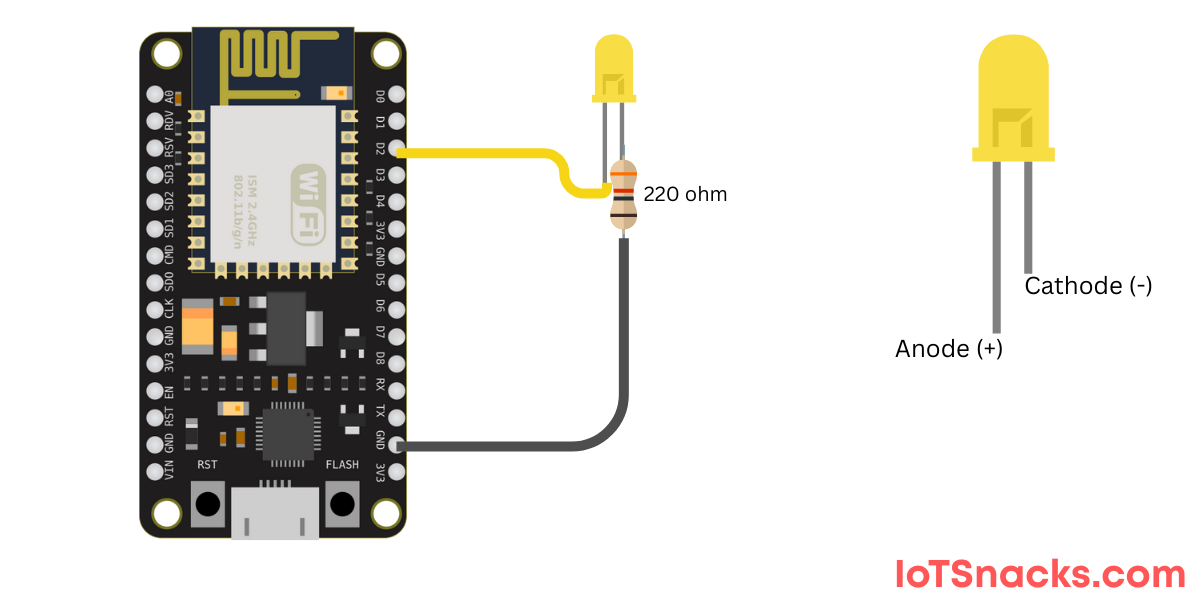
How LDR Works? & Circuit Connection
An LDR’s resistance:
- High in darkness (acts like an insulator).
- Low in bright light (acts like a conductor).
Since ESP8266 cannot directly measure resistance, we use a voltage divider circuit to convert resistance changes into voltage that the ESP8266 can read using its ADC pin (A0).
- Connect one side of LDR to 5V/3.3V.
- Connect the other side of LDR to A0 (ADC pin).
- Also connect a 10kΩ resistor between A0 and GND.
This forms a voltage divider where the LDR and resistor share voltage depending on light intensity.

Arduino Code for LDR with ESP8266
// LDR with ESP8266 Example
// Reads light intensity and prints to Serial Monitor
int ldrPin = A0; // LDR connected to analog pin A0
int ldrValue = 0; // Variable to store LDR value
void setup() {
Serial.begin(115200); // Start serial communication
}
void loop() {
ldrValue = analogRead(ldrPin); // Read value from LDR
Serial.print("Light Intensity: ");
Serial.println(ldrValue); // Print value on Serial Monitor
delay(1000); // Wait 1 second
}
Step-by-Step Code Explanation
int ldrPin = A0;- Defines the pin connected to LDR (A0).
- ESP8266 has only one analog pin (A0).
int ldrValue = 0;- Creates a variable to store the sensor reading.
void setup()- Runs once when ESP8266 starts.
Serial.begin(115200);→ Opens serial communication at 115200 baud rate to see values on Serial Monitor.
void loop()- Repeats continuously.
analogRead(ldrPin);→ Reads light level (value between 0 and 1023).- 0 = complete darkness.
- 1023 = very bright light.
Serial.print&Serial.println→ Show the sensor value in Arduino Serial Monitor.delay(1000);→ Updates reading every 1 second.
Upload and Test
- Connect ESP8266 to PC.
- Select the correct COM port in Arduino IDE.
- Upload the code.
- Open Serial Monitor (set baud rate: 115200).
- Cover and uncover the LDR → You’ll see values changing in real time.
Real-Life Applications
- Automatic lights → Turn ON street lights when dark.
- Smart curtains → Adjust blinds based on sunlight.
- Light-based alarms → Detect intruders by light changes.
- IoT projects → Send LDR data to cloud dashboards (ThingSpeak, Blynk, MQTT).
Troubleshooting
- Getting constant values? → Check LDR-resistor wiring.
- Very low sensitivity? → Use a different resistor (5k–20kΩ).
- Wrong values? → Ensure ESP8266 is reading from A0 (only analog pin).
Conclusion
In this tutorial, you learned how to:
- Connect an LDR to ESP8266 using a voltage divider.
- Write and understand code to read light intensity values.
- Test values in the Arduino Serial Monitor.
This simple setup is the foundation of many IoT projects like automatic lights, smart homes, and energy-saving systems. 🚀
What is the range of analog values from LDR on ESP8266?
It ranges from 0 (dark) to 1023 (bright light).
Can I connect LDR directly without resistor?
No, you must use a resistor to form a voltage divider.
Can ESP8266 detect exact brightness (lux)?
No, it only gives relative light intensity. For exact lux values, use sensors like BH1750.