Now Reading: RGB LED with ESP8266 (NodeMCU / Wemos D1 Mini)
-
01
RGB LED with ESP8266 (NodeMCU / Wemos D1 Mini)
RGB LED with ESP8266 (NodeMCU / Wemos D1 Mini)

Introduction
RGB LEDs are special LEDs that combine Red, Green, and Blue in one package. By adjusting the brightness of each color, you can create millions of colors 🌈.
In this tutorial, you’ll learn:
- The types of RGB LEDs (Common Anode & Common Cathode)
- ESP8266 PWM and GPIO pins
- Circuit diagram and connections
- Arduino code to control RGB LED
- Step-by-step explanation
This project is beginner-friendly and helps you understand analogWrite (PWM) on ESP8266.
What You Need
- ESP8266 board (NodeMCU or Wemos D1 Mini)
- 1 x RGB LED (common cathode recommended for beginners)
- 3 x 220Ω resistors
- Breadboard and jumper wires
- Arduino IDE
Understanding RGB LEDs
There are two types of RGB LEDs:
- Common Cathode (CC):
- All negative legs (GND) are connected together.
- Apply HIGH (3.3V) on Red/Green/Blue pins to light them.
- Common Anode (CA):
- All positive legs are connected together.
- Apply LOW (0V) on Red/Green/Blue pins to light them.
👉 For simplicity, we’ll use Common Cathode in this tutorial.
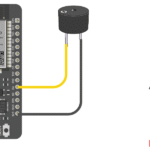
Circuit Connections
Text diagram (NodeMCU pins):
- RGB LED Common Cathode → GND
- RGB LED Red pin → D1 (GPIO5) through 220Ω resistor
- RGB LED Green pin → D2 (GPIO4) through 220Ω resistor
- RGB LED Blue pin → D3 (GPIO0) through 220Ω resistor

Arduino Code: RGB LED with ESP8266
// RGB LED with ESP8266 (NodeMCU/Wemos)
// Common Cathode RGB LED example
int redPin = D1; // GPIO5
int greenPin = D2; // GPIO4
int bluePin = D3; // GPIO0
void setup() {
pinMode(redPin, OUTPUT);
pinMode(greenPin, OUTPUT);
pinMode(bluePin, OUTPUT);
}
// Function to set color
void setColor(int redValue, int greenValue, int blueValue) {
analogWrite(redPin, redValue); // 0 - 1023
analogWrite(greenPin, greenValue);
analogWrite(bluePin, blueValue);
}
void loop() {
setColor(1023, 0, 0); // Red
delay(1000);
setColor(0, 1023, 0); // Green
delay(1000);
setColor(0, 0, 1023); // Blue
delay(1000);
setColor(1023, 1023, 0); // Yellow (Red + Green)
delay(1000);
setColor(0, 1023, 1023); // Cyan (Green + Blue)
delay(1000);
setColor(1023, 0, 1023); // Magenta (Red + Blue)
delay(1000);
setColor(1023, 1023, 1023); // White (All ON)
delay(1000);
setColor(0, 0, 0); // OFF
delay(1000);
}
Step-by-Step Code Explanation
Define pins
int redPin = D1;
int greenPin = D2;
int bluePin = D3;
Pins Setup
pinMode(redPin, OUTPUT);
pinMode(greenPin, OUTPUT);
pinMode(bluePin, OUTPUT);
Custom Function
void setColor(int redValue, int greenValue, int blueValue) {
analogWrite(redPin, redValue);
analogWrite(greenPin, greenValue);
analogWrite(bluePin, blueValue);
}
analogWrite()generates a PWM signal (0–1023 on ESP8266).- Higher values = more brightness.
Loop colors
- First Red, then Green, then Blue.
- Mix two colors (Yellow, Cyan, Magenta).
- All ON for White.
- All OFF for LED OFF.
Output
- The RGB LED will cycle through Red, Green, Blue, Yellow, Cyan, Magenta, White, and OFF, changing every second.
Real-Life Applications
- Mood lights and smart home lighting
- IoT-based LED strips
- Weather visualization (red = hot, blue = cold 🌡️)
- Notification systems (color indicates status)
Troubleshooting
- If colors look wrong, swap the wires of R, G, B.
- If LED doesn’t light up:
- Check resistors.
- Ensure you’re using 3.3V logic (not 5V directly).
- Confirm whether your LED is common cathode or anode (invert logic for common anode).
Conclusion
With just a few lines of code, you learned how to control an RGB LED with ESP8266. Using PWM and color mixing, you can create endless lighting effects for your IoT projects.
Next, you can expand this project by:
- Adding potentiometers to control colors manually.
- Using a web server on ESP8266 to change colors from your phone.
- Controlling an RGB LED strip (WS2812B/NeoPixel).
Can I use analogWrite() on all GPIO pins?
Yes, ESP8266 supports software PWM on all digital pins.
What’s the PWM range on ESP8266?
analogWrite() accepts values from 0 (OFF) to 1023 (FULL brightness).
My RGB LED shows inverted colors. Why?
You might be using a Common Anode LED. In that case, use 1023 - value in analogWrite.